
Blog

Thomas Strottner
More and more companies are seeing the benefits of the public cloud and are picking up speed in their transformation to a modern IT architecture. Nevertheless, this journey is also associated with risks: Who can access the company's and customers' data? How to ensure that no workloads have been compromised? In addition, personal data is exposed to a particular risk due to the so-called CLOUD Act, which is fundamentally incompatible with the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
The CLOUD Act (short for Clarifying Lawful Overseas Use of Data Act) requires US companies to disclose data stored or processed outside the United States to authorized US authorities without a court order. The law regulates the handling of corporate data that is physically located outside the United States, but for which a US company is responsible. Under the CLOUD Act, this data is treated as if it were stored on servers in the United States. This means that the sensitive personal data of EU citizens is no more secure than corporate data such as trade secrets to intellectual property. The CLOUD Act thus conflicts with laws in Germany, such as the Unfair Competition Act, and the European Union, above all the GDPR. In 2020, The Schrems II ruling by the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) invalidated the Privacy Shield that previously regulated EU-US data transfers, opening a period of uncertainties for companies and consumers.
Confidential computing is a new technology that allows data to remain encrypted even during processing, i.e. in RAM. So for the first time, data can really stay end-to-end encrypted --- at rest, in transit, and in use. In addition, confidential computing provides remote attestation features to ensure that only specific code is executed and no workloads have been compromised. With confidential computing hardware such as AMD SEV-SNP, AWS Nitro Enclaves, and, in the future, Intel TDX or Arm Realms, this technology can also be used for so-called confidential VMs, which are already available from most cloud providers. As data stays encrypted also in memory, even datacenter admins with physical access to a server, cannot get access to any information. By combining confidential hardware with the right infrastructure software, companies can greatly reduce the trusted computing base (TCB) and fully remove the cloud provider from the trust equation.
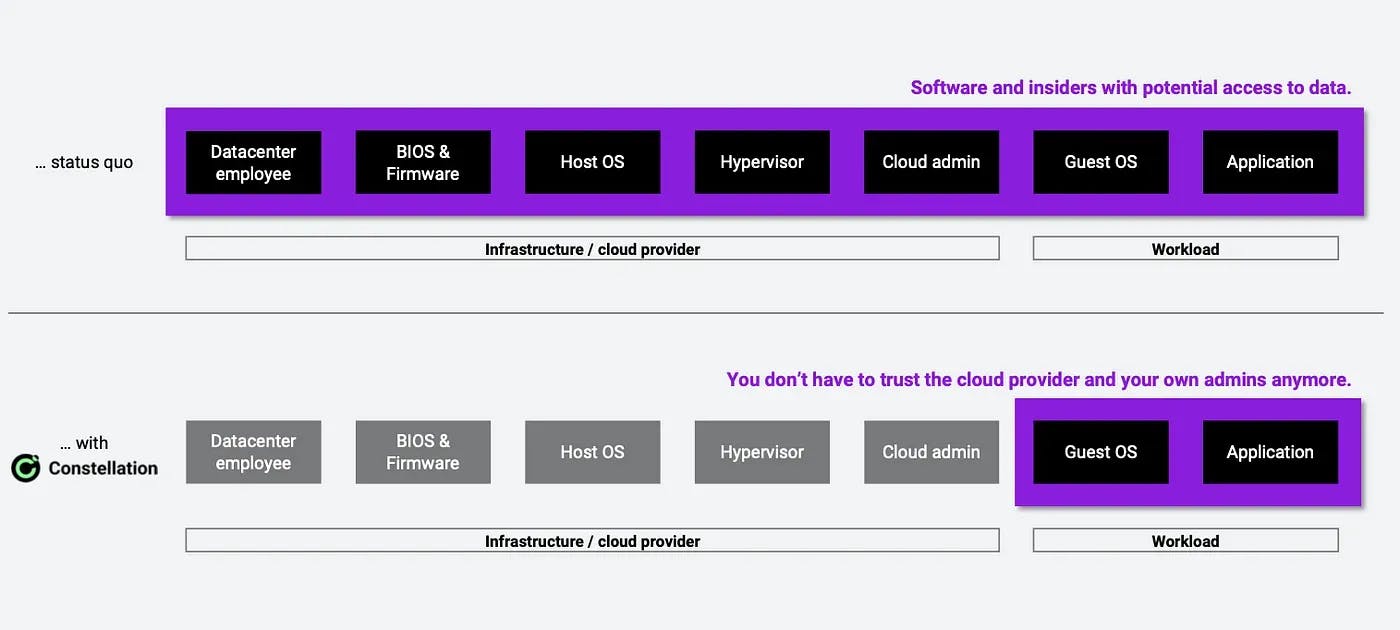
The end-to-end encryption and strong security architecture do not only resolve the issues that arise from the CLOUD Act. The GDPR also requires "privacy by design" (using technologies such as encryption) and "data minimization" to protect personal information. With state-of-the-art confidential computing, companies fulfill these requirements and significantly strengthen GDPR compliance.
European cloud providers claim that the solution to the "Schrems II problem" is using a European datacenter. However, the CLOUD Act is not the only concern when it comes to using someone else's computers for processing your and your customers. Besides data privacy requirements, growing cybersecurity concerns and costs of data breaches --- over $4.2M on average in 2021--- are great concerns for CEOs, CTOs, and CISOs. With confidential computing, companies do not have to trust the entity that runs their applications. In addition, they can ensure the integrity of their workloads. Even though this might sound magical, it's not a fantasy, but something that can be achieved today.
Edgeless Systems now offers Constellation, a confidential and CNCF-certified Kubernetes, which enables scalable use of Confidential VMs across cloud environments. With confidential K8s, the entire data flow remains encrypted end-to-end and clusters are isolated from the infrastructure in seconds. So companies no longer have to trust their cloud infrastructure provider. In addition, users get cryptographic proof that no data has been compromised by hackers or cloud providers. This not only strengthens compliance but also brings security to unprecedented levels.
"With Constellation, all data always remains encrypted and enterprises no longer need to trust cloud providers. The Kubernetes distribution is CNCF certified and therefore compatible with all containers and tools. So I get a completely shielded Kubernetes that is no different at all in user experience. Best of all, with remote attestation for the entire cluster, data protection and compliance officers can prove that cloud workloads are truly secure."
- Felix Schuster, CEO, Edgeless Systems
Author: Thomas Strottner